What's Current in
Science + Technology
Image
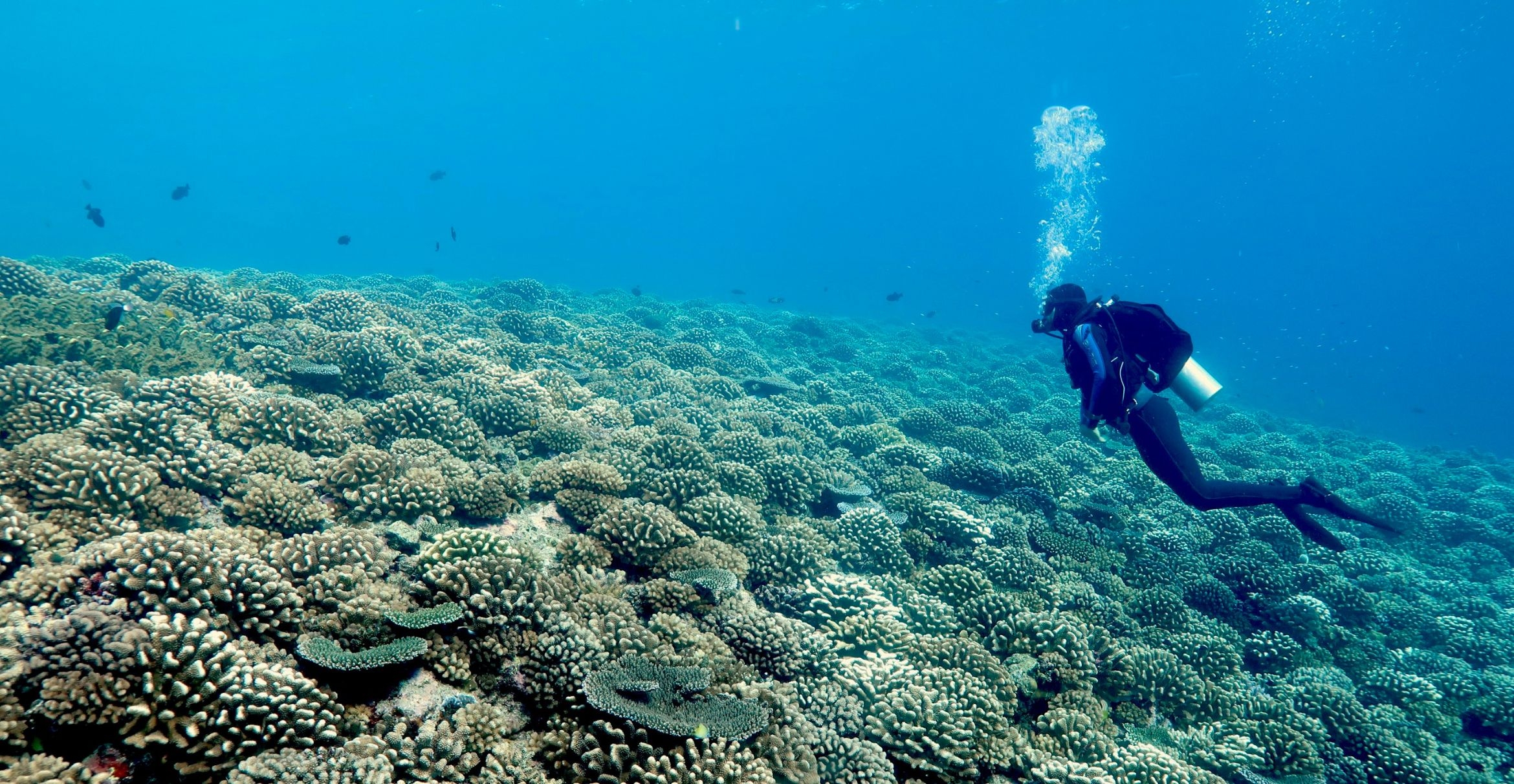

Photo Credit
Andrew Thurber
The structural complexity of a healthy coral reef provides habitat for a diversity of lifeforms.
Image

Photo Credit
Matt Perko
Emily Jacobs
Image
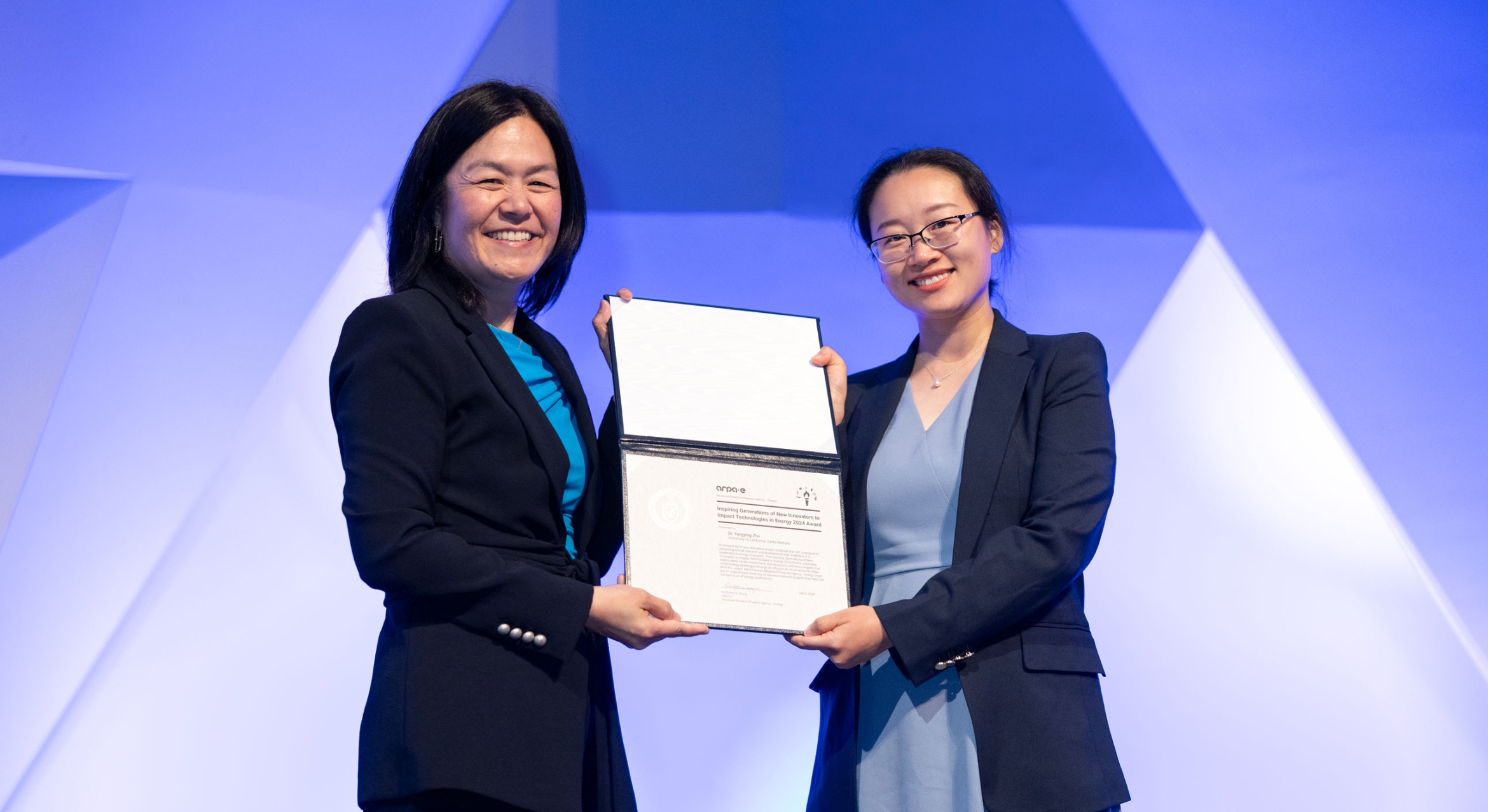

Photo Credit
James Badham
Yangying Zhu (right), assistant professor in the UCSB Mechanical Engineering Department, receives her award certificate from ARPA-E Program Director Dr. Evelyn Wang at the National Academy of Sciences, in Washington, D.C.
Image

Photo Credit
Udra via iStock
Image
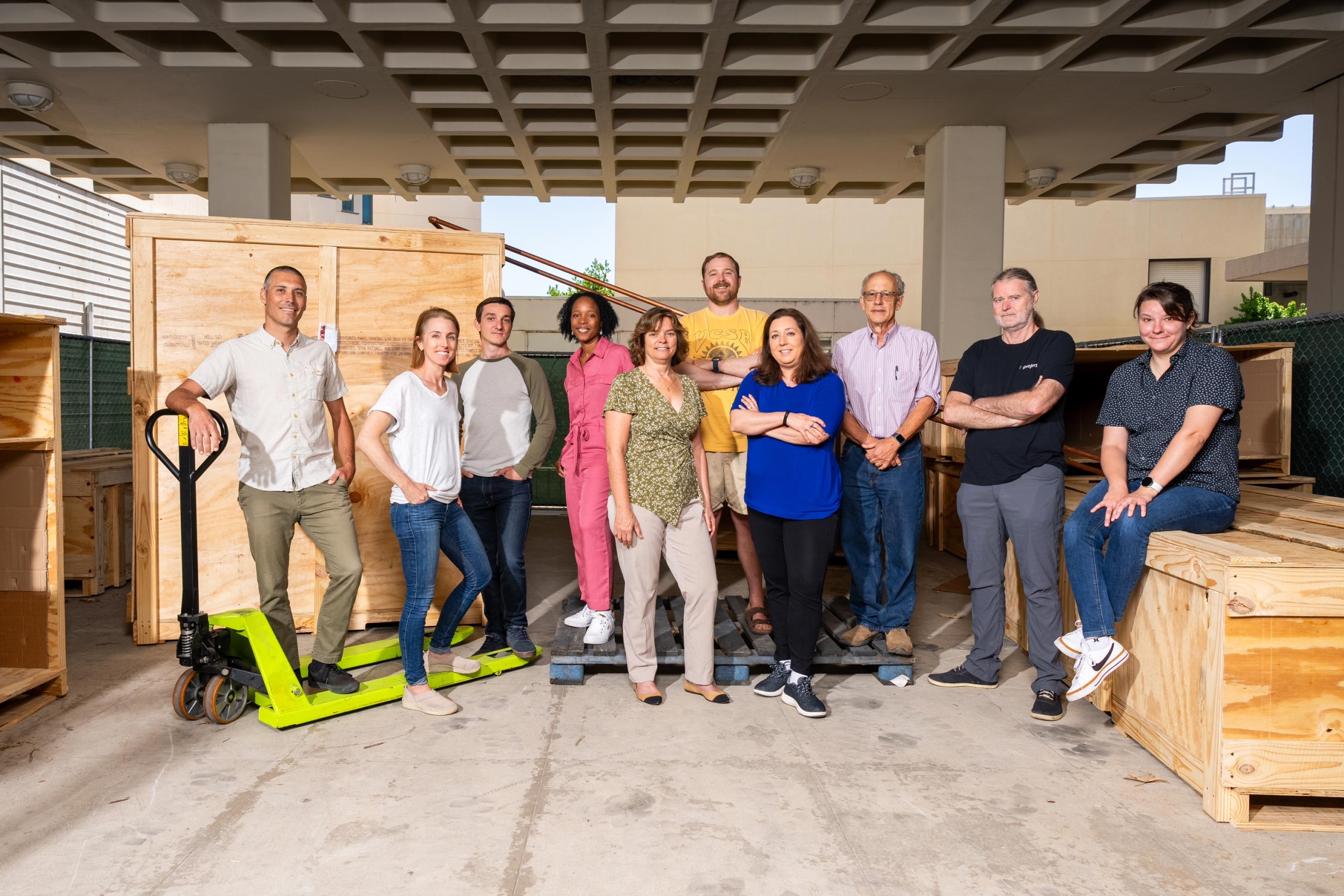

Photo Credit
Jeff Liang
UCSB ExFAB staff and senior participants, from left, Oliver Vining, Elaine Kirschke, Jean-Marie Volland, Nathalie Elisabeth, Sherylle Mills Englander, Max Wilson, Michelle O'Malley, Joel Rothman, Niels Volkmann and Carolyn Mills.
Image
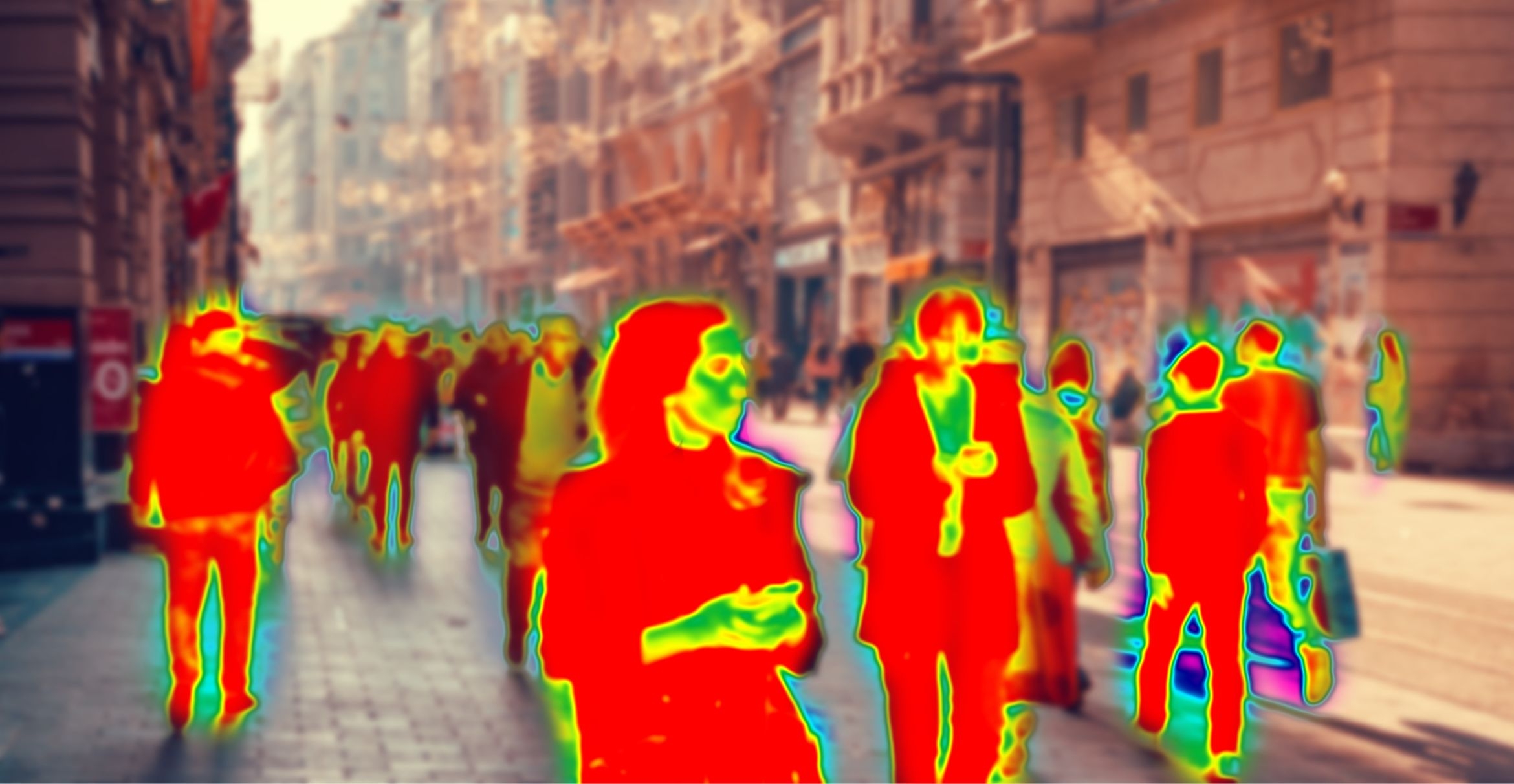

Photo Credit
Ildar Abulkhanov via iStock
It’s not quite heat vision, but mosquitoes do use thermal infrared to find human hosts.