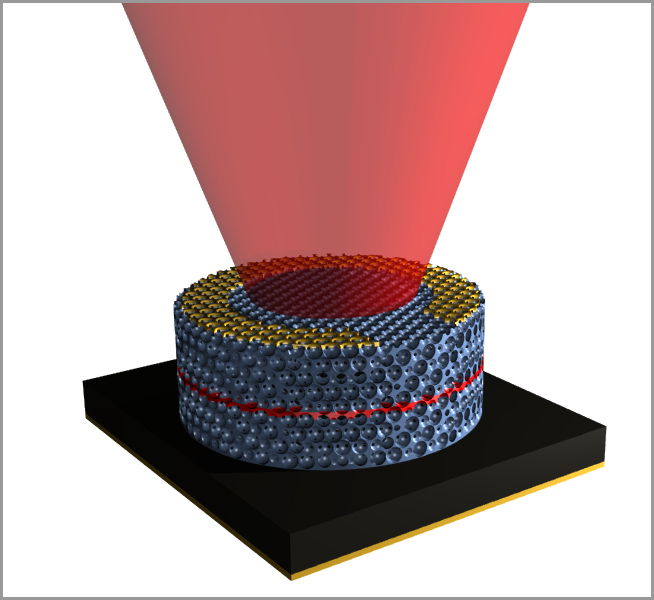

In an advance that could open new avenues for solar cells, lasers, metamaterials, and more, a scientist at UC Santa Barbara collaborated with a team from the University of Illinois to demonstrate the first optoelectronically active 3-D photonic crystal. The research is published in this week's online version of the journal Nature Materials.
"The importance of this research lies in the bridging between photonics and electronics," said co-author Pierre Wiltzius, the Susan and Bruce Worster Dean of Science and professor of physics at UCSB. "Photonic crystals have interesting optical properties on their own, but having the capability to control them electronically opens up entirely new classes of applications."
Photonic crystals are materials that can control or manipulate light in unexpected ways thanks to their unique physical structures. Photonic crystals can induce unusual phenomena and affect photon behavior in ways that traditional optical materials and devices can't. They are popular materials of study for applications in lasers, solar energy, LEDs, metamaterials, and more.
Previous attempts at making 3-D photonic crystals have resulted in devices that are only optically active –– that is, they can direct light –– but not electronically active, meaning they can't turn electricity to light or vice versa. However, this team's photonic crystal has both properties.
"We've discovered a way to change the three-dimensional structure of a well-established semiconductor material to enable new optical properties while maintaining its very attractive electrical properties," said Paul Braun, a professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Illinois who led the research effort.
"With our approach to fabricating photonic crystals, there's a lot of potential to optimize electronic and optical properties simultaneously," said Erik Nelson, a former graduate student in Braun's lab who now is a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard University. "It gives you the opportunity to control light in ways that are very unique –– to control the way it's emitted and absorbed, or how it propagates."
To create a 3-D photonic crystal that is both electronically and optically active, the researchers started with a template of tiny spheres packed together. Then, they deposited gallium arsenide (GaAs), a widely used semiconductor, through the template, filling in the gaps between the spheres.
The GaAs grows as a single crystal from the bottom up, a process called epitaxy. Epitaxy is used in industry to create flat, two-dimensional films of single-crystal semiconductors, but Braun's group developed a way to apply it to an intricate three-dimensional structure.
"The key discovery here was that we grew single-crystal semiconductor through this complex template," said Braun, who also is affiliated with the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, and with the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory at Illinois.
"Gallium arsenide wants to grow as a film on the substrate from the bottom up, but it runs into the template and goes around it," said Braun. "It's almost as though the template is filling up with water. As long as you keep growing GaAs, it keeps filling the template from the bottom up until you reach the top surface."
The epitaxial approach eliminates many of the defects introduced by top-down fabrication methods, a popular pathway for creating 3-D photonic structures. Another advantage is the ease of creating layered heterostructures. For example, a quantum well layer could be introduced into the photonic crystal by partially filling the template with GaAs, and then briefly switching the vapor stream to another material.
Once the template is full, the researchers remove the spheres, leaving a complex, porous 3-D structure of single-crystal semiconductor. Then they coat the entire structure with a very thin layer of a semiconductor with a wider bandgap to improve performance and prevent surface recombination.
To test their technique, the group built a 3-D photonic crystal LED –– the first such working device. Now, the researchers are working to optimize the structure for specific applications. The LED demonstrates that the concept produces functional devices, but by tweaking the structure or using other semiconductor materials, researchers can improve solar collection or target specific wavelengths for metamaterials applications or low-threshold lasers.
"From this point on, it's a matter of changing the device geometry to achieve whatever properties you want," Nelson said. "It really opens up a whole new area of research into extremely efficient or novel energy devices."
The U.S. Department of Energy and the Army Research Office supported this work. Other Illinois faculty involved in the project are electrical and computer engineering professors James Coleman and Xiuling Li, and materials science and engineering professor John Rogers.
Prior to his appointment as Dean of Science at UCSB, Wiltzius was the director of the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, and professor of materials science and engineering and physics at the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign from 2001 to 2008. He joined Lucent Technologies-Bell Laboratories (formerly AT&T Bell Laboratories) in 1984, where he most recently was the director of semiconductor physics research.
Related Links