Taming Satellite Data

More than 700 imaging satellites orbit the Earth, and every day they beam vast amounts of information to databases on the ground. There’s just one problem: While the geospatial data could help researchers and policymakers address critical challenges, only those with considerable wealth and expertise can access it.
Now, a team of scientists, including UC Santa Barbara’s Tamma Carleton, has devised a machine learning system to tap the problem-solving potential of satellite imaging. The tool employs low-cost, user friendly technology that could bring access and analytical power to researchers and governments worldwide. The study appears in the journal Nature Communications.
“Millions of satellite images are taken of our planet every day, but actually using this information to solve global problems like climate change and poverty eradication is difficult,” explained Carleton, an assistant professor and environmental economist at UCSB’s Bren School of Environmental Science & Management.
“The trick is how to translate the data into usable insights without having a human comb through every single image,” said co-author Esther Rolf, a doctoral student at UC Berkeley. “We designed our system for accessibility, so that one person should be able to run it on a laptop, without specialized training, to address their local problems.”
Until now, Carleton noted, the technology to translate images into useful information — like income in a village or water quality across the planet’s rivers — has been in the hands of a few well-funded research teams in wealthy countries.
The project was a collaboration between the Global Policy Lab, at Berkeley’s Goldman School of Public Policy and Benjamin Recht’s research team in Berkeley’s electrical engineering and computer sciences department. In addition to Carleton, the co-authors include Berkeley Ph.D. graduates Jonathan Proctor, now at Harvard; Ian Bolliger, now at the Rhodium Group; and Vaishaal Shankar, now at Amazon; as well as current Berkeley Ph.D. student Miyabi Ishihara.
Their collaboration has been brought together disciplines that often look at the world in different ways and speak different languages: computer science, environmental and climate science, statistics, economics and public policy.
But they have been guided by a common interest in creating an open access tool that democratizes the power of technology, making it usable even by communities and countries that lack resources and advanced technical skill. “It’s like Ford’s Model T, but with machine learning and satellites,” said co-author Solomon Hsiang, director of the Global Policy Lab. “It’s cheap enough that everyone can now access this new technology.”
MOSAIKS: Improving lives, protecting the planet
The system that emerged is called MOSAIKS, short for Multi-Task Observation using Satellite Imagery & Kitchen Sinks. It ultimately could have the power to analyze hundreds of variables drawn from satellite data — from soil and water conditions to housing, health and poverty — at a global scale.
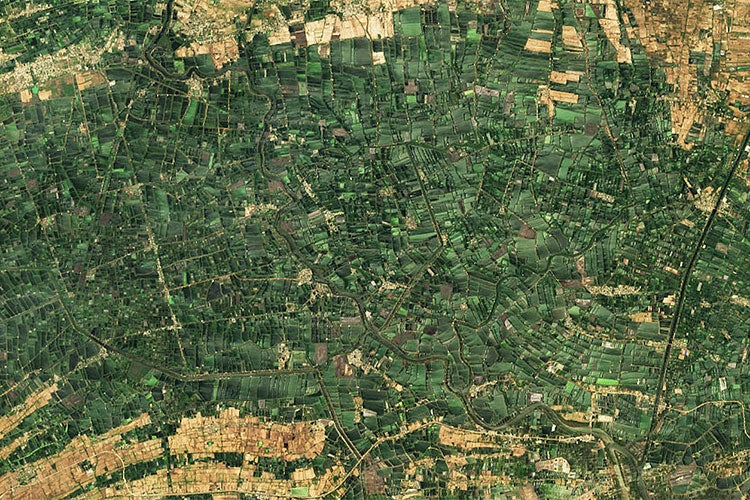

A satellite image shows hundreds of green aquaculture ponds in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Geospatial imaging holds enormous potential for developing nations to address challenges related to agriculture, poverty, health and human migration.
Photo Credit: JOSHUA STEVENS AT NASA EARTH OBSERVATORY; USGS
As the paper details, MOSAIKS was able to replicate with reasonable accuracy reports prepared at great cost by the U.S. Census Bureau. It also has enormous potential in addressing development challenges in low-income countries, and to help scientists and policymakers understand big-picture environmental change.
“Climate change is diffuse and difficult to see at any one location, but when you step back and look at the broad scale, you really see what is going on around the planet,” said Hsiang, who also serves as co-director of the multi-institution Climate Impact Lab.
For example, he said, the satellite data could give researchers deep new insights into expansive rangeland areas such as the Great Plains in the U.S. and the Sahel in Africa, or into regions such as Greenland or Antarctica that may be shedding icebergs as temperatures rise.
“These areas are so large, and to have people sitting there and looking at pictures and counting icebergs is really inefficient,” Hsiang explained. But with MOSAIKS, “you could automate that and track whether these glaciers are actually disintegrating faster, or whether this has been happening all along.”
For a government in the developing world, the technology could help guide even routine decisions, such as where to build roads.
“A government wants to build roads where the most people are and the most economic activity is,” Hsiang said. “You might want to know which community is underserved, or the condition of existing infrastructure in a community. But often it’s very difficult to get that information.”
The challenge: Organizing trillions of bytes of raw satellite data
The growing fleet of imaging satellites beam data back to Earth 24/7 — some 80 terabytes every day, according to the research, a number certain to grow in coming years.
But often, imaging satellites are built to capture information on narrow topics — supplies of fresh water, for example, or the condition of agricultural soils. And the data doesn’t arrive as a collection of neat, orderly images. It’s raw data, a mass of binary information. Researchers who access the data have to know what they’re looking for.
Merely storing so many terabytes of data requires a huge investment. Distilling the layers of data embedded in the images requires additional computing power and advanced human expertise to tease out strands of information that are coherent and useful to other researchers, policymakers or funding agencies.
Inevitably, exploiting satellite images is largely limited to scholars or agencies in wealthy nations, the authors said.
“If you’re an elite professor, you can get someone to build your satellite for you,” said Hsiang. “But there’s no way that a conservation agency in Kenya is going to be able to access the technology and the experts to do this work.
“We wanted to find a way to empower them. We decided to come up with a Swiss Army Knife — a practical tool that everyone can access.”
Like Google for satellite imagery, sort of
Especially in low-income countries, one dimension of poverty is a paucity of data. But even communities in the U.S. and other developed countries usually don’t have ready access to geospatial data in a convenient, usable format for addressing local challenges.
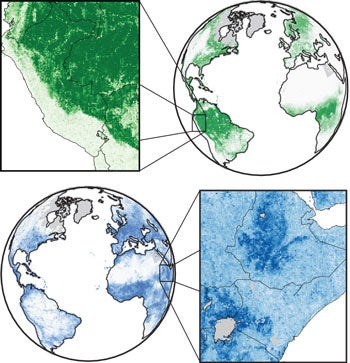
The illustrations show how the MOSAIKS machine learning system predicts, in fine detail, forest cover (above, in green) and population (below).
Photo Credit: COURTESY OF THE AUTHORS
Machine learning opens the door to solutions. In a general sense, machine learning refers to computer systems that use algorithms and statistical modeling to learn on their own, without step-by-step human intervention. What the new research describes is a system that can assemble data delivered by many satellites and organize it in ways that are accessible and useful.
There are precedents for such systems: Google Earth Engine and Microsoft’s Planetary Computer are both platforms for accessing and analyzing global geospatial data, with a focus on conservation. But, Rolf said, even with these technologies, considerable expertise is often required to convert the data into new insights.
The goal of MOSAIKS is not to develop more complex machine learning systems, Rolf said. Rather, its innovation is in making satellite data widely useable for addressing global challenges. The team did this by making the algorithms radically simpler and more efficient.
MOSAIKS starts with learning to recognize minuscule patterns in the images — Hsiang compares it to a game of Scrabble, in which the algorithm learns to recognize each letter. In this case, however, the tiles are minuscule pieces of satellite image, 3 pixels by 3 pixels.
But MOSAIKS doesn’t conclude “this is a tree” or “this is pavement.” Instead, it recognizes patterns and groups them together, said co-author Jonathan Proctor. It learns to recognize similar patterns in different parts of the world.
When thousands of terabytes from hundreds of sources are analyzed and organized, researchers can choose a village or a country or a region and draw out organized data that can touch on themes as varied as soil moisture, health conditions, human migration and home values.
In a sense, Hsiang said, MOSAIKS could do for satellite databases what Google in the early days did for the Internet: Map the data, make it accessible and user-friendly at low cost, and perhaps make it searchable.
Creating a living atlas of global data
The authors see the potential for MOSAIKS to evolve in powerful and elegant directions.
Hsiang imagines the data being collected into computer-based, continually evolving atlases. Turn to any given “page,” and a user could access broad, deep data about conditions in a country or a region.
The team is working to build MOSAIKS into a tool for real-time monitoring of the world’s most pressing problems, from climate change to the spread of infectious disease. “We are working on a global database and user-friendly website where researchers and practitioners can interact with MOSAIKS and generate their own, novel measures of what matters for their communities,” Carleton said.
Rolf envisions a system that can take the stream of data from humanity’s fleet of imaging satellites and remote sensors and transform it into a flowing, real-time portrait of Earth and its inhabitants, continually in a state of change. We could see the past and the present, he said, and so discern emerging challenges and address them.
“We’ve sent so much stuff to space,” Hsiang said. “It’s an amazing achievement. But we can get a lot more bang for our buck for all of this data that we’re already pulling down. Let’s let the world use it in a useful way. Let’s use it for good.”